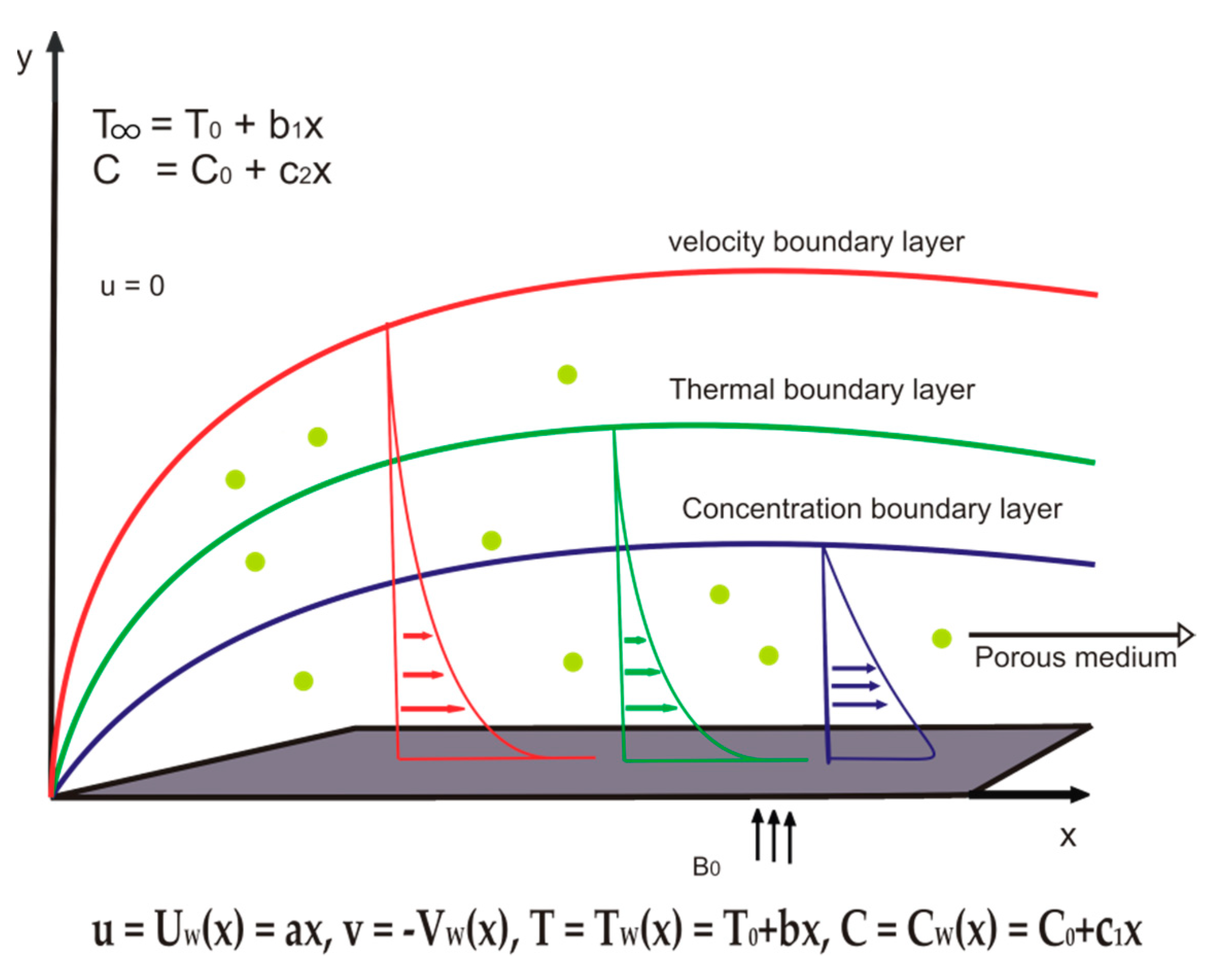
Mca Free Full Text Magneto Mixed Convection Of Williamson Nanofluid Flow Through A Double Stratified Porous Medium In Attendance Of Activation Energy Html
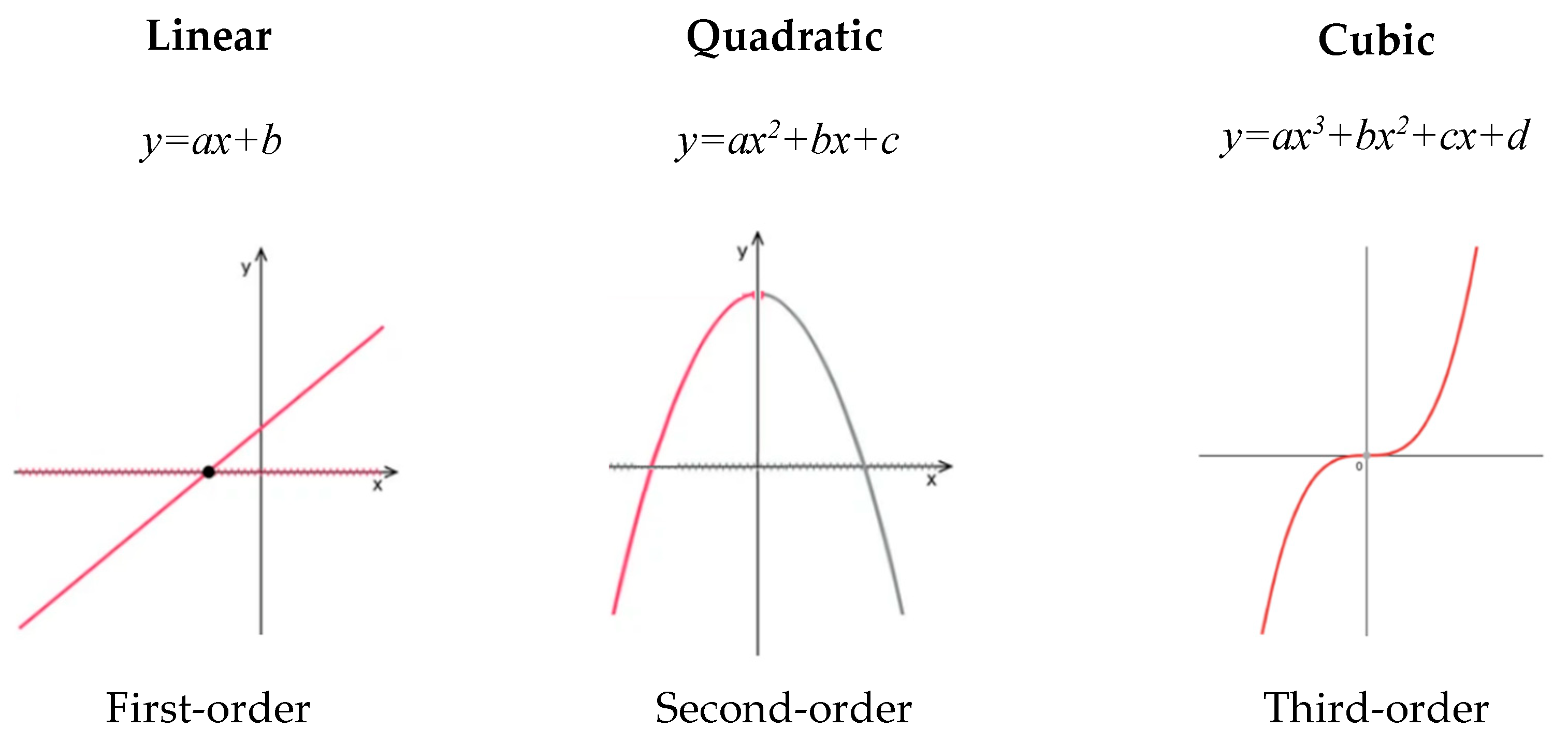
As said before, the graph of a quadratic function is known as a parabola Having calculated the roots, the vertexand the yinterception, one can now plot the graph The graph of//socraticorg/questions/5a4332f611ef6b503cd Please see below Explanation Let us convert the two equations into vertex form y = ax2 4bxc = a(x2 4abx (2ab)2 −4a2b2) c
Y=ax^2+bx+c examples
Y=ax^2+bx+c examples-Y=ax^2bxc with sliders Conic Sections Parabola and Focus exampleIn this video explaining vtu engineering mathematics third semester problemThis problem is second degree finding a, b and c parametersThis method is very i
Exploring Parabolas Y Ax 2 Bx C
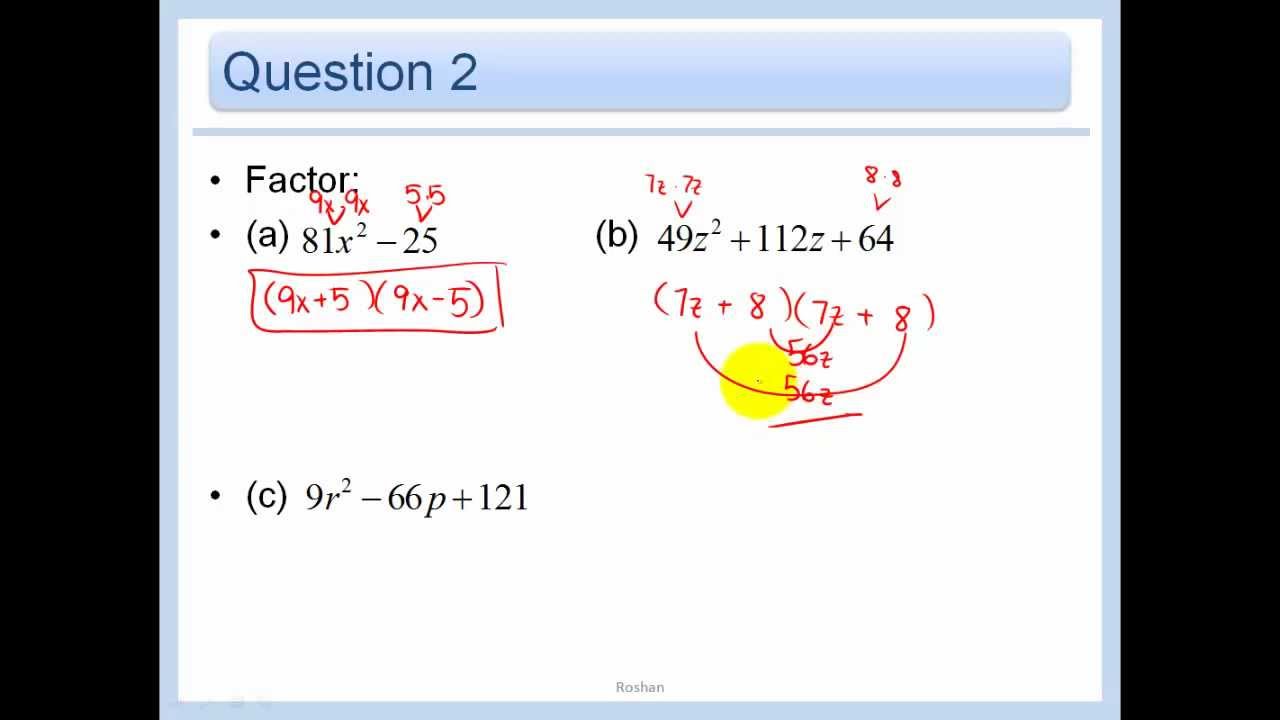
These are all horizontal lines crossing the y axis at the c value Example 2 Let a = 1 and b = 0 We have a normal parabola with the base of the parabola on the yaxis at the value ofTrinomials of the Form ax^2 bx c Study this pattern for multiplying two binomials Example 1 Factor 2 x 2 – 5 x – 12 Begin by writing two pairs of parentheses For the first positions, find twoQuestion Give one (1) illustrative example for each concept on transforming quadratic functions Write your answer in general form y = ax^2bxc and its equivalent vertex form y=a(x
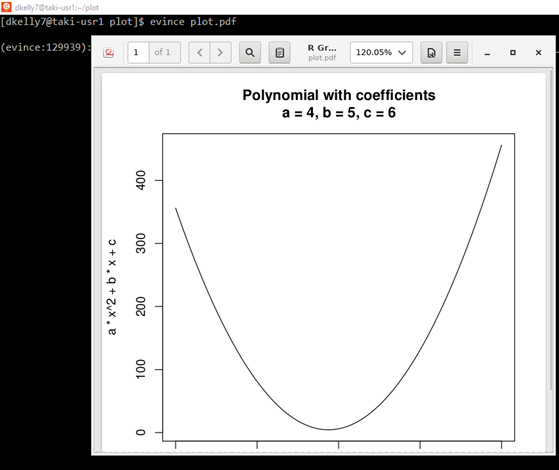
Graph y = ax^2 bx c Conic Sections Parabola and Focus exampleY = ax2 bx c y = a x 2 b x c Rewrite the equation as ax2 bx c = y a x 2 b x c = y ax2 bxc = y a x 2 b x c = y Subtract y y from both sides of the equation ax2 bxc−y = 0 a x 2Related » Graph » Number Line » Similar » Examples simplify y=ax^{2}bxc en image/svgxml Related Symbolab blog posts Practice Makes Perfect Learning math takes
Y=ax^2+bx+c examplesのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 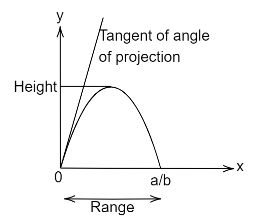 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 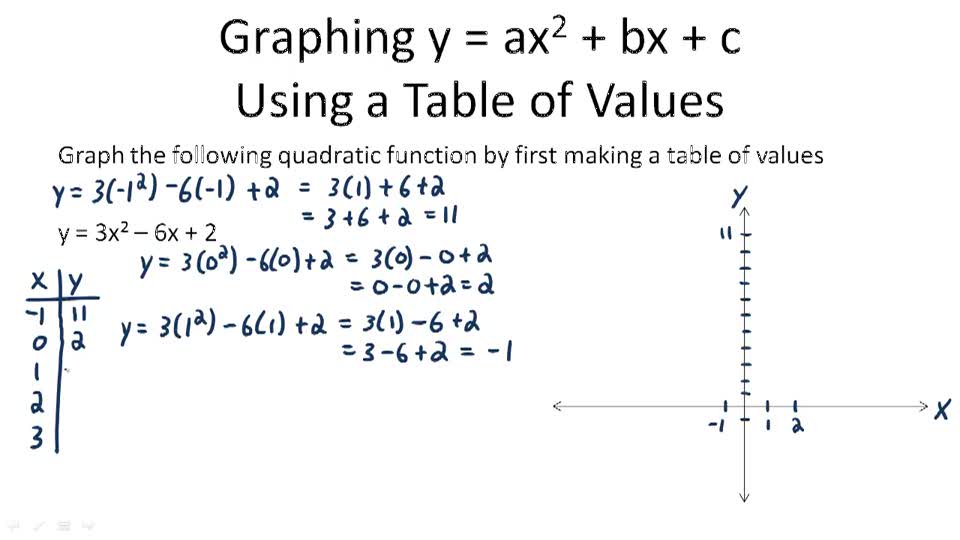 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 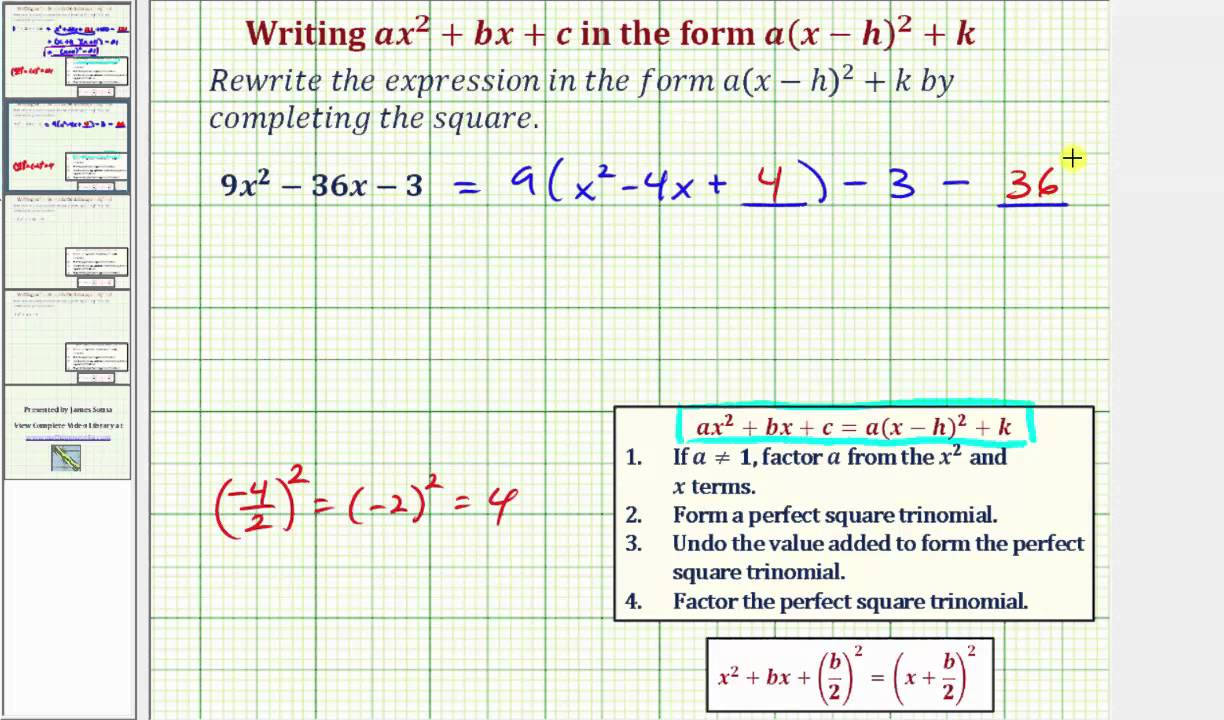 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 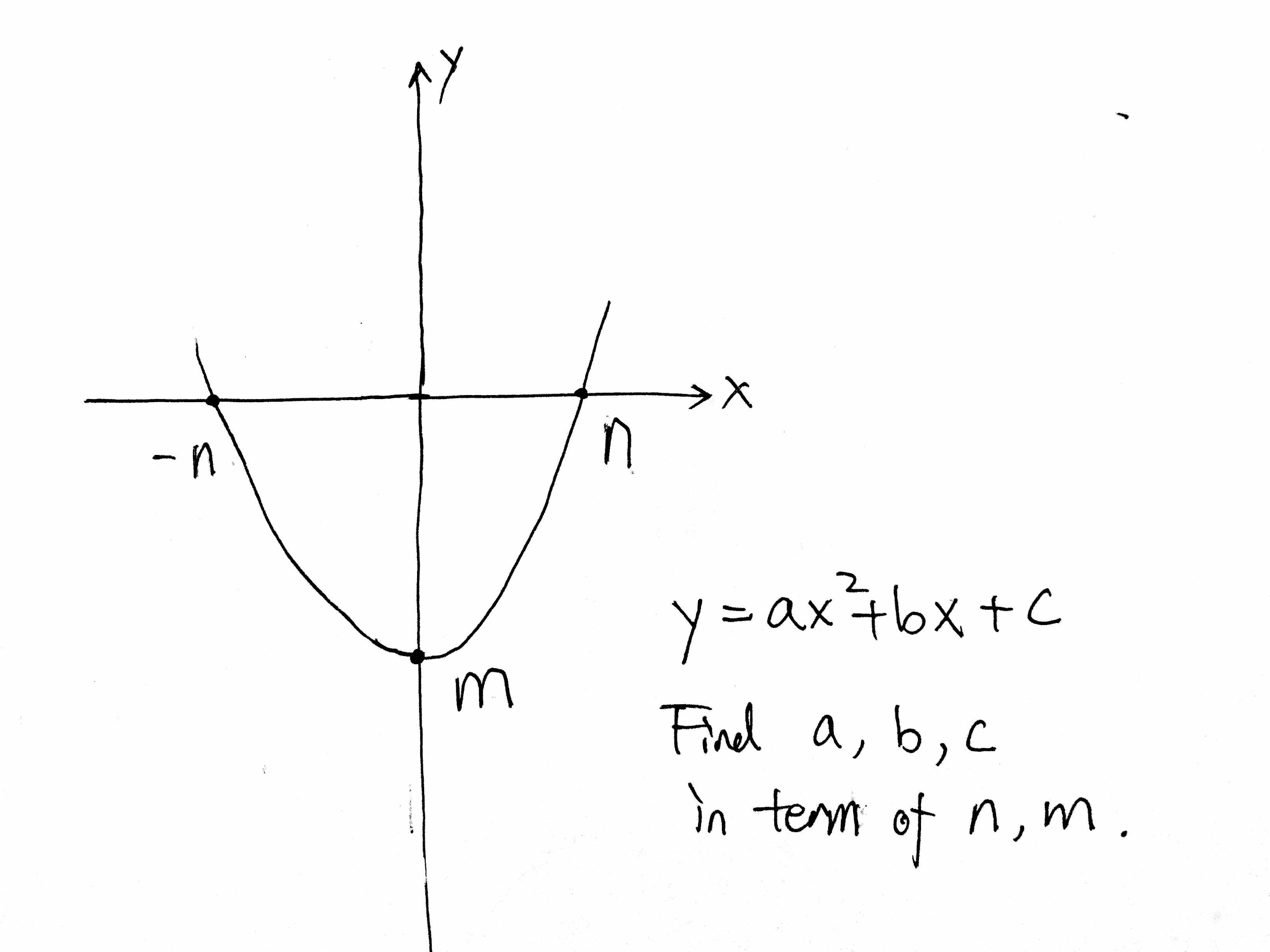 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 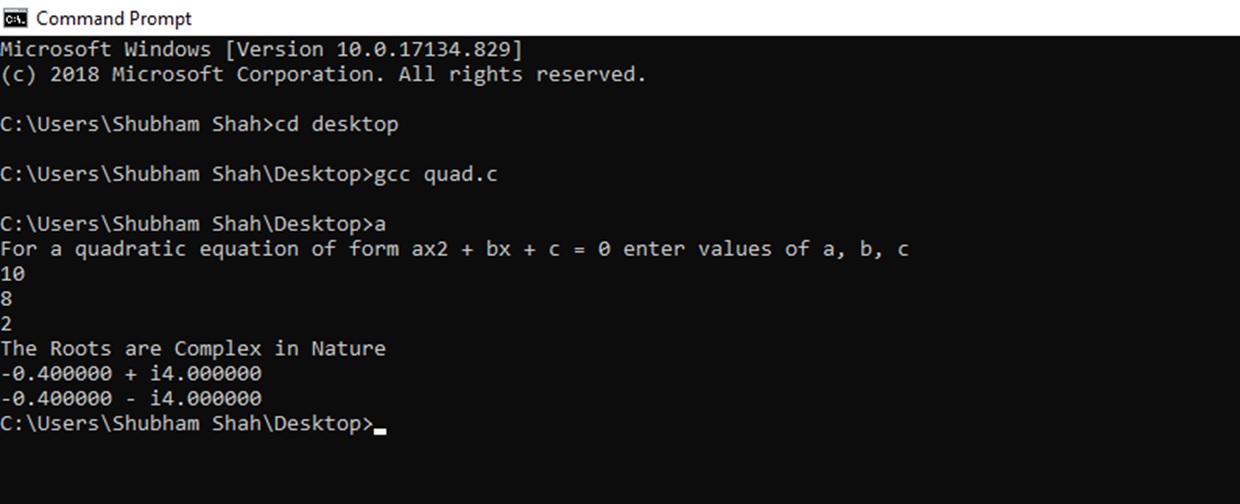 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 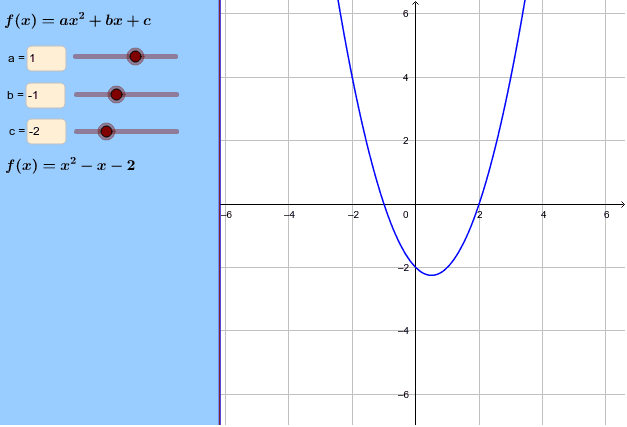 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 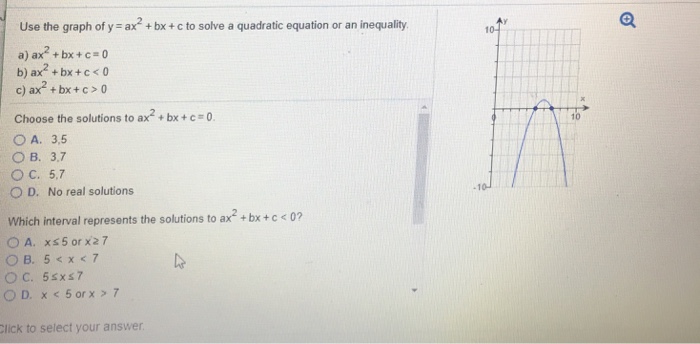 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 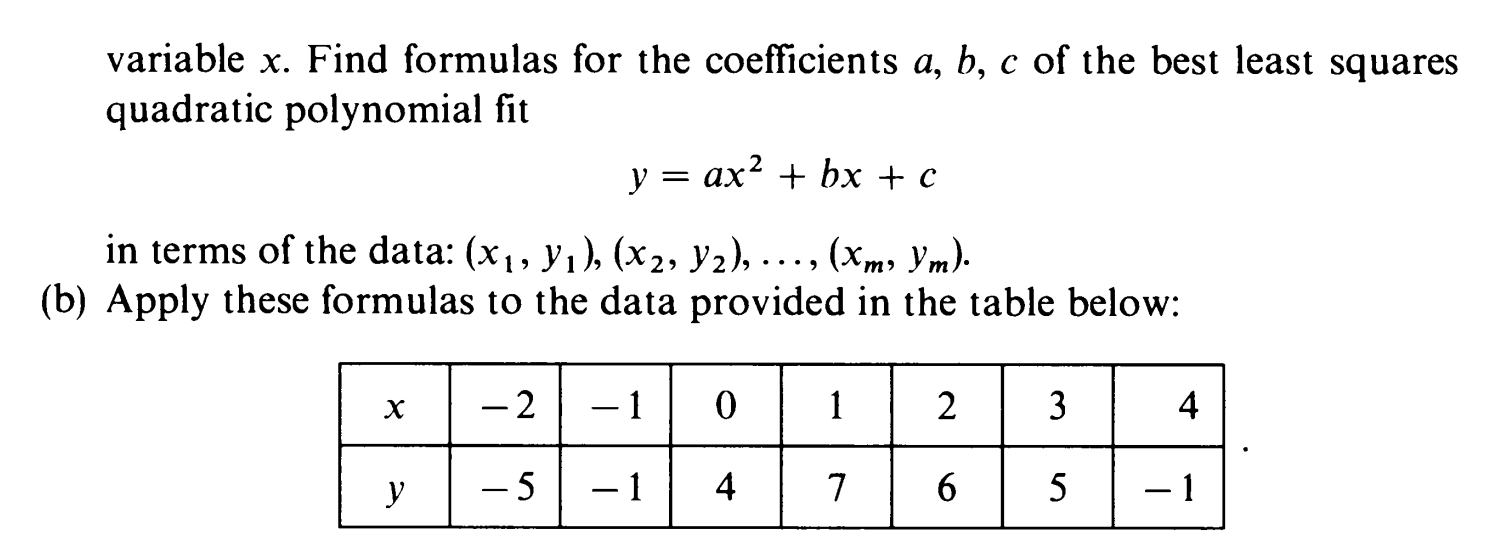 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 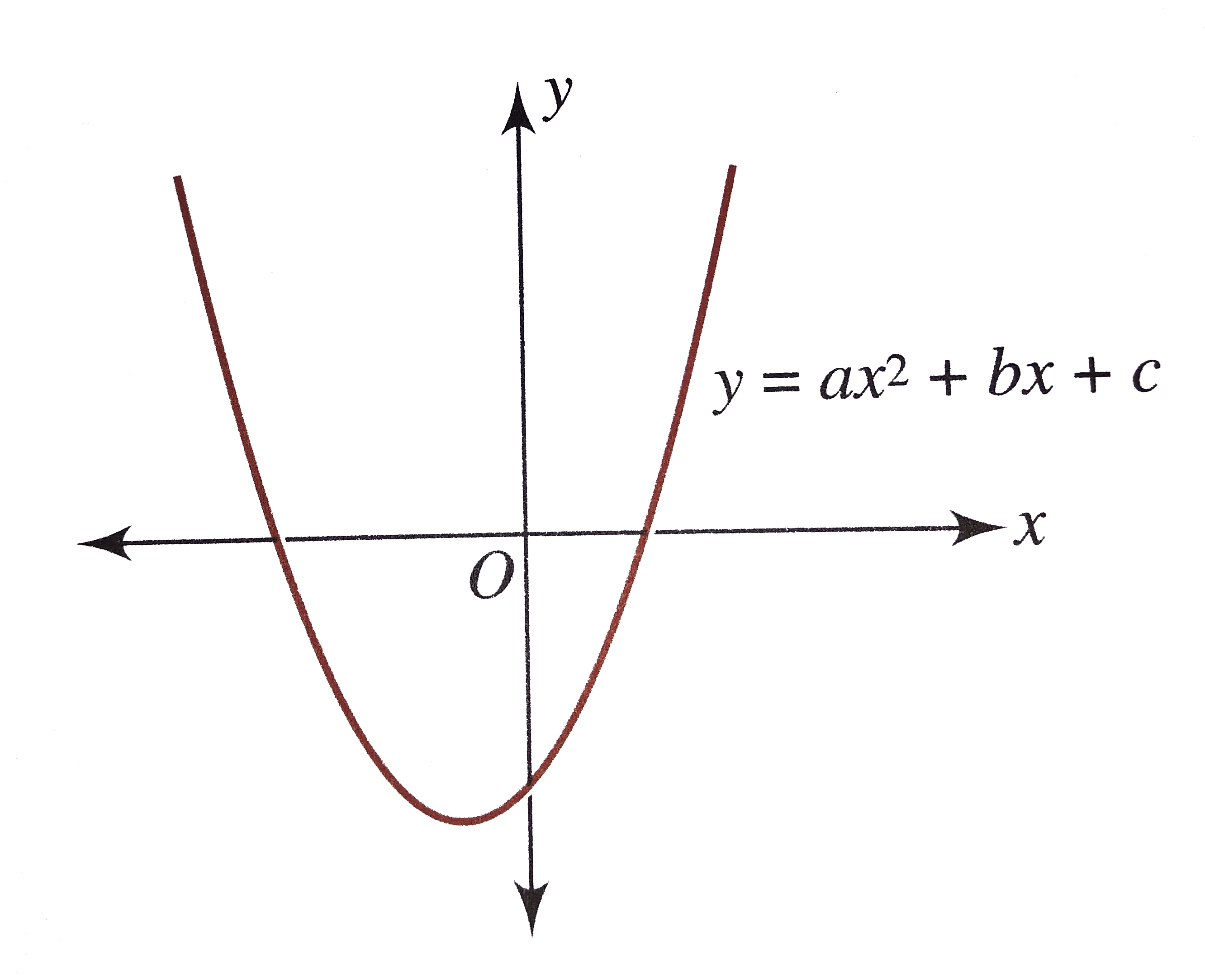 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 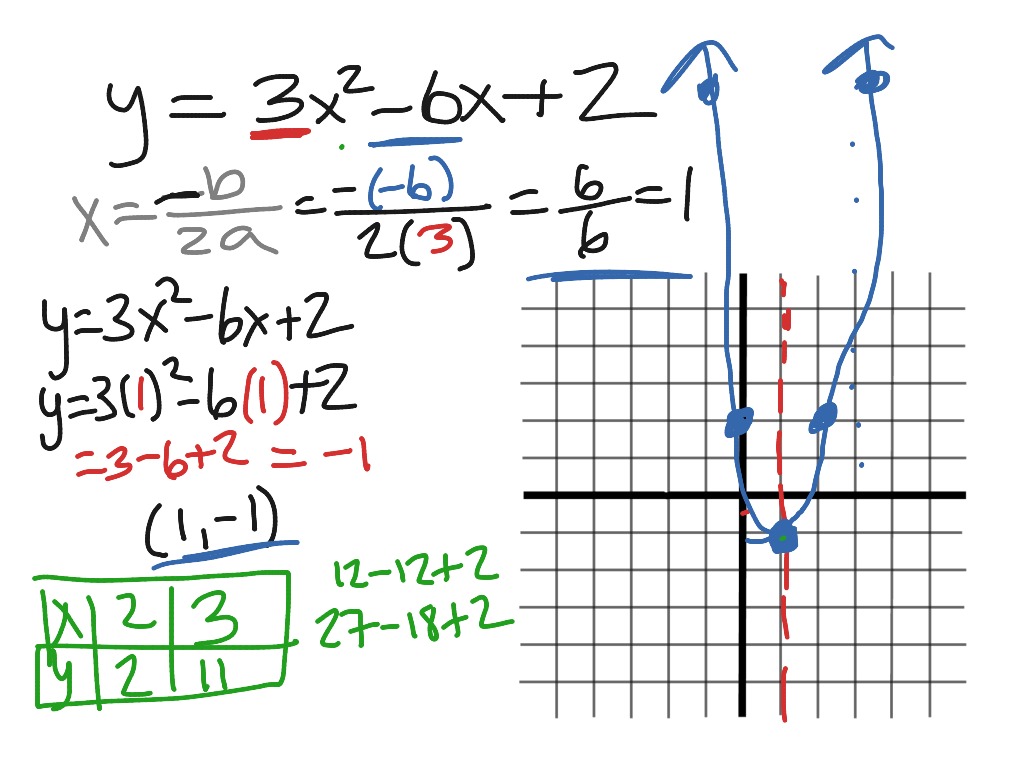 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | 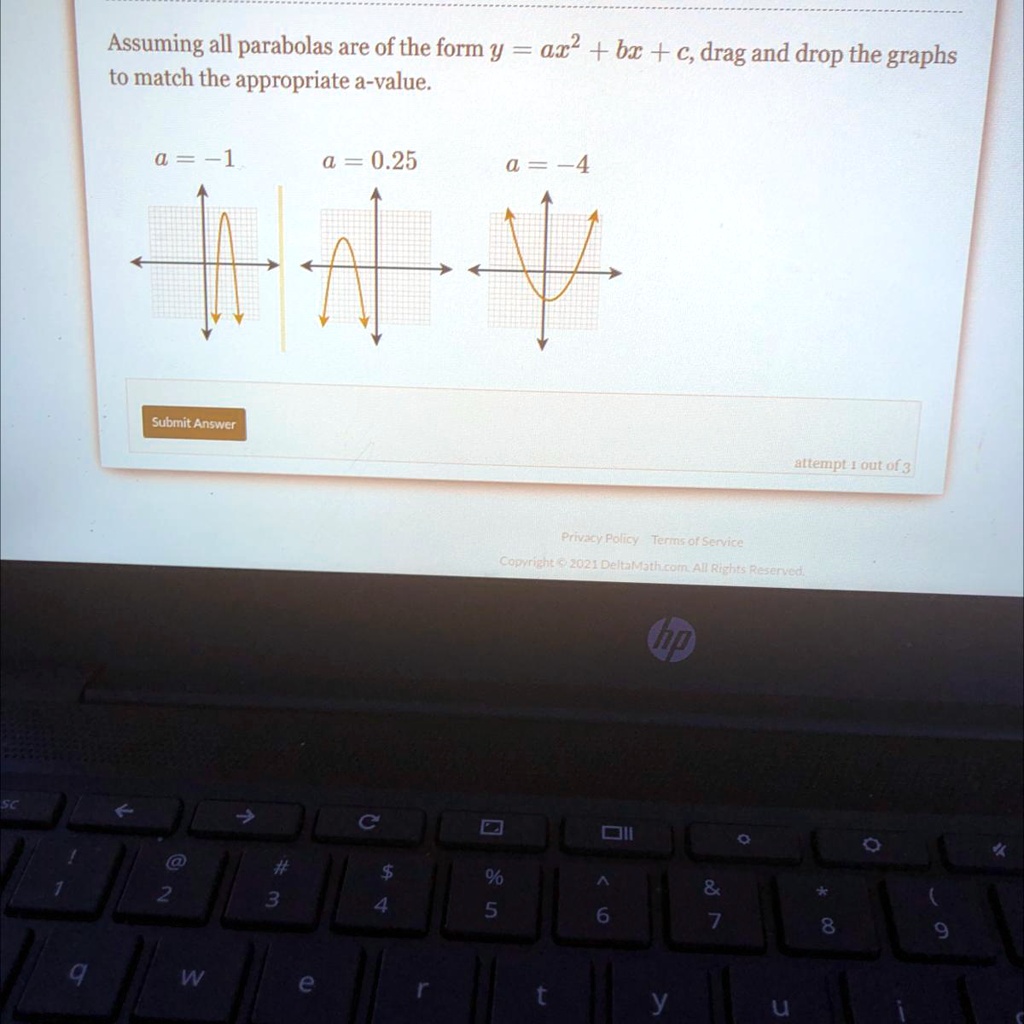 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
 The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances | The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |  The Trajectory Of A Projectile In A Vertical Plane Is Y Ax Bx 2 Where A B Are Constants And X And Y Are Respectively The Horizontal And Vertical Distances |
Find stepbystep Algebra solutions and your answer to the following textbook question A student says that the graph of y = ax^2 bx c gets wider as a increases a Use examples to show thatExample 1 Find the vertex of a parabola, y=3x212x12 Solution Given parabola equation y=3x212x12 The given parabola equation is of the standard form y=ax2bxc By comparing
Incoming Term: y=ax^2+bx+c examples,




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿